Allergy Cough or Something More?
A persistent allergy cough can be disruptive and uncomfortable, often leading to frustration, especially when it lingers throughout the day. While an ongoing cough may point to seasonal allergies, it could signal a more complex health issue.
An allergy cough is typically dry and triggered by airborne allergens like pollen, dust, or pet dander, resulting from irritation in the respiratory system rather than mucus buildup. Recognizing the difference between an allergy cough and other types of coughs is essential to managing symptoms effectively.
Key Characteristics of an Allergy Cough
An allergy cough can often be mistaken for a common cold, but understanding the distinct characteristics can help individuals manage it more effectively. Unlike other types of coughs, an allergy cough is usually persistent and occurs alongside other allergy symptoms, such as itchy eyes and sneezing. Notably, this type of cough tends to worsen in environments where the allergen is present. Some key indicators that your cough may be allergy-related include:
- Coughing that is persistent and lasts for more than two weeks
- No accompanying fever or body aches
- Occurs during specific times of the year or in certain environments
- Triggered by exposure to known allergens
- Improved by taking allergy medication

Common Causes of a Persistent Cough
A persistent cough may be caused by various underlying conditions, some of which need specific treatment to resolve fully. While allergies are a common cause, a cough that doesn’t improve or comes with additional symptoms may indicate another health issue. Recognizing these other potential sources can help you understand when to seek further evaluation or treatment.
Here are some common causes of a persistent cough:
- Respiratory Infections: Colds, bronchitis, and pneumonia can cause lingering coughs. Seek medical attention if your cough is accompanied by a fever, chills, or difficulty breathing.
- Acid Reflux: A type of acid reflux known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause a chronic cough. If you experience heartburn along with your cough, consult your doctor.
- Smoking: Long-term exposure to smoke can irritate the lungs and lead to chronic coughing. If you smoke, quitting can significantly improve both your overall health and persistent cough.
- Lung Conditions: Chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or other lung conditions may lead to a persistent cough. If you have a history of these conditions or are experiencing additional symptoms such as shortness of breath, consult your doctor.
- Medication Side Effects: Certain medications, like ACE inhibitors (commonly prescribed for high blood pressure), can cause a persistent dry cough as a side effect. If you’re taking an ACE inhibitor and experiencing a chronic cough, consult your doctor to discuss your options.
Allergy Cough vs. Other Coughs: How to Spot the Difference
Determining if your cough is due to allergies or something more concerning can be tricky. Here’s a breakdown to help you identify different types of coughs based on symptoms and triggers.
Allergy Cough
As mentioned before, an allergy cough is typically dry and persistent, triggered by exposure to allergens. It may also come with other symptoms, such as itchy eyes and sneezing.
Common Cold Cough
A cough caused by a common cold often comes with additional symptoms such as a sore throat, runny nose, and congestion. It can be wet or dry and usually improves within a week or two.
Flu Cough
Similar to a cold cough, a flu cough often accompanies other symptoms like fever, body aches, and fatigue. It can be severe and last for several weeks.
Pneumonia Cough
A cough caused by pneumonia is typically wet and can produce yellow or green mucus. It may also come with symptoms such as chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. Seek medical attention if you suspect you have pneumonia.
Asthma Cough
Asthma can cause coughing, especially at night or during exercise. It may also come with wheezing and shortness of breath. If you have a history of asthma or are experiencing these symptoms, consult your doctor.
Treatment Options for an Allergy Cough
If you suspect your cough is allergy-related, several treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent them from worsening. Over-the-counter options like antihistamines, decongestants, and nasal corticosteroids are often effective for mild to moderate symptoms, providing relief from sneezing, itching, and post-nasal drip.
For individuals with more severe or persistent allergies, immunotherapy — such as allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy — can offer long-term relief by gradually building the body’s tolerance to specific allergens. Consulting with an allergist can help you find the most effective treatment approach for your unique needs.
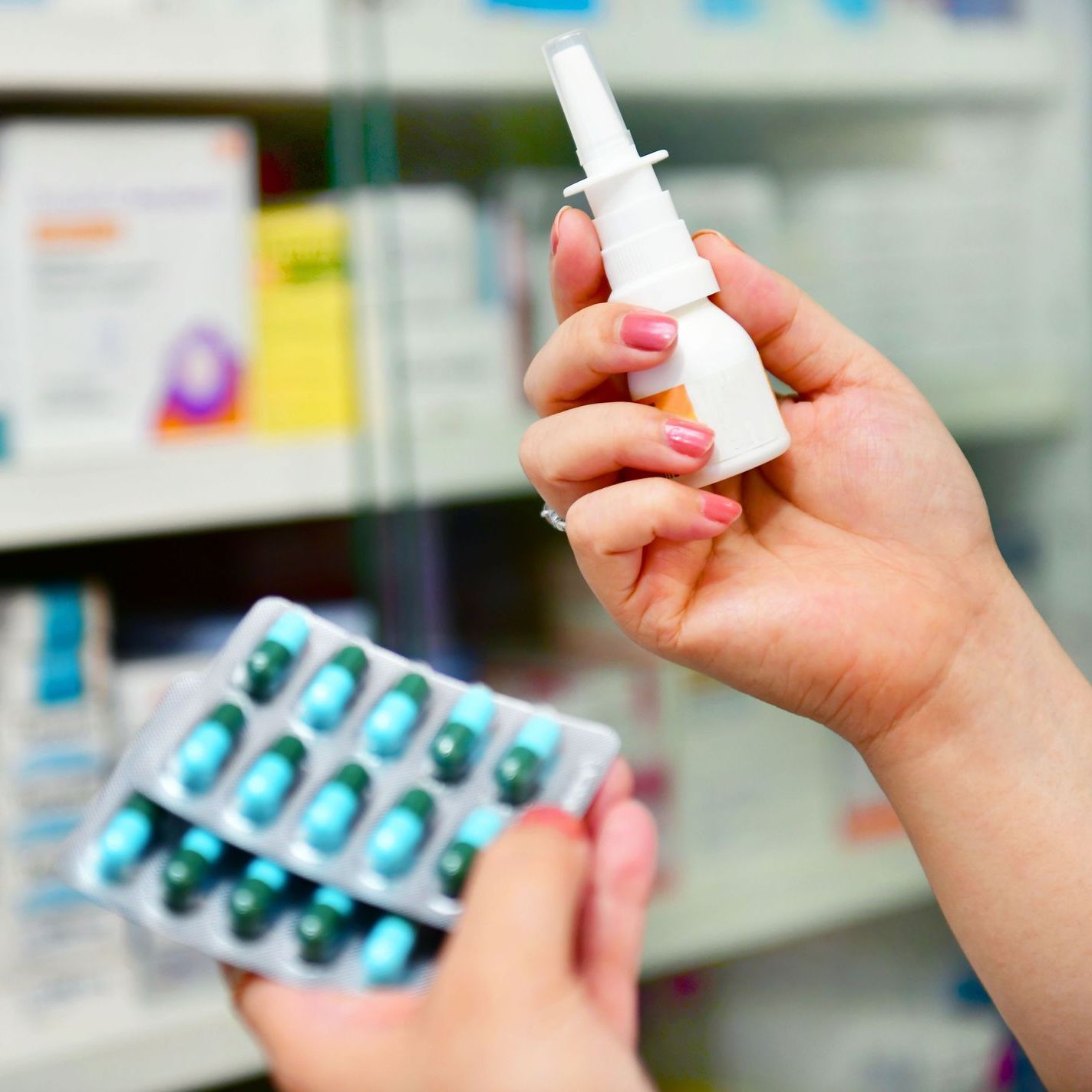
Treat Your Allergy Cough at Northeast Allergy
Don’t let an allergy cough disrupt your life any longer. At Northeast Allergy, our specialists are dedicated to providing personalized care tailored to your unique needs. Whether you’re dealing with persistent allergies or need a comprehensive plan to manage your symptoms, we’re here to help you find relief and improve your well-being. Schedule an appointment with one of our allergists today and take the first step toward breathing easier.